Overview
African Bank, established in 2016, operates retail banks throughout South Africa. Originally an unsecured lender, African Bank was restructured in 2016 to provide services directly to consumers under licenses from the South African Reserve Bank (SARB). Consumers engage with African Bank services through an omni‑channel approach which includes physical branches and digital operations such as web, mobile applications, and call centers.
Challenge
African Bank sees its digital innovations and product offerings as a way both to cut overall costs and to provide added value to banking customers. The initial architecture supporting the various digital features available across its channels was monolithic in nature. As such, when developers wanted to launch new features they had to go through a cumbersome and time‑consuming process including both approvals and lengthy testing. African Bank recognized the benefits it could achieve by migrating from a monolithic to microservices architecture but needed to find a core component that could provide a variety of functionality across the entire omni‑channel platform, while being easily deployed within a container framework. The bank also needed commercial support for the component they identified as the core of their microservices architecture. Finally, African Bank needed a better way to manage its APIs in order to extend the functionality provided by the microservices to current and potential partner companies in the FinTech industry.
Solution
As African Bank pursued a transition to a microservices architecture, it came across the NGINX Microservices Reference Architecture (MRA) which not only provided a clear path on how to build and deploy the architecture, but also identified NGINX Plus as the centralized component it needed to proxy requests from end users to the services deployed in its container-based framework.
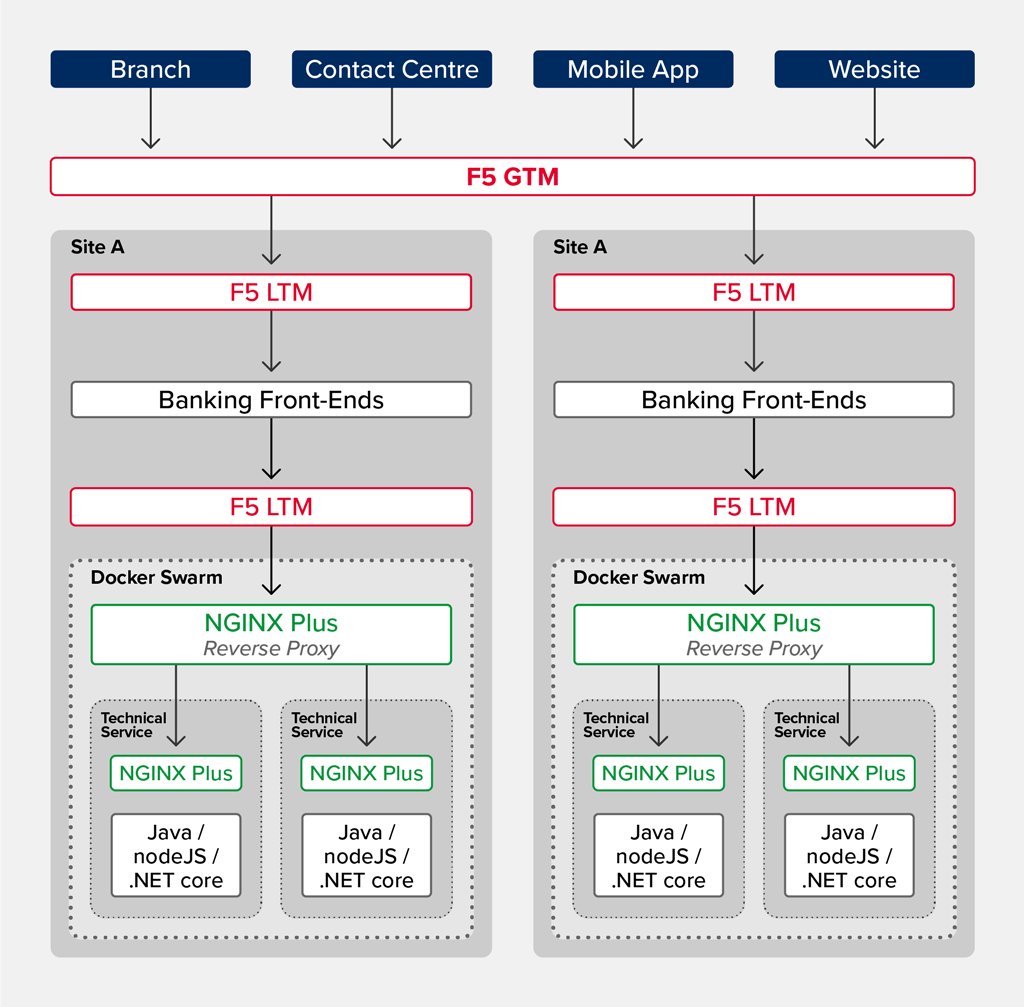
Before African Bank selected NGINX Plus, its monolithic architecture employed a variety of tools including typical application delivery controllers, like F5 BIG-IP for global traffic management, and F5 WAF for security. Rather than replacing those tools, though, the bank saw NGINX Plus augmenting existing infrastructure through powerful features like reverse proxy and load balancing. What NGINX Plus provided, ultimately, was a powerful multi‑functional component which addressed all of their use cases and could be easily deployed in a flexible manner.
As a single component providing many functions, NGINX Plus freed African Bank from the need to choose and deploy a variety of single‑function point solutions, like Apigee for API management, which would have radically complicated overall architectural management and maintenance. Further, NGINX Plus can be deployed on bare metal, virtual machines, and most importantly, in Docker containers which are critical to any microservices architecture providing unprecedented flexibility in how the bank deployed its revamped infrastructure.
NGINX Plus provides not only a high‑performing reverse proxy and load balancer, but also a way to manage the availability, authentication, metering, security, and other aspects of the APIs the bank makes available to its many FinTech partners. The architecture the African Bank engineers created is a dynamic, scalable solution employing Docker containers, NGINX Plus instances, and customized code that enabled developers to take full ownership of deployed services that can be dropped into the architecture in real time.
Results
Improved Delivery Time for New Features
Since deploying NGINX Plus, African Bank engineers and operations have seen a significant improvement in the turnaround time for delivering requested functionality and new features across their omni‑channel platform. In the past, the lead time for creating new servers and deploying new load balancers was significant. With NGINX Plus, they have been able to put the control of application and feature deployment into the developers’ hands, who can now spin up an NGINX Plus instance on demand and employ it for their specific use case.
Within the microservices architecture, these use cases can be encapsulated in a service that is linked to the Docker container. Through a dynamically configurable NGINX conf file that is automatically updated by reading service events through the Docker API, new features that are encapsulated as microservices can be launched in real time and without any server downtime. This means African Bank can quickly roll out features across their omni‑channel platform, keeping them competitive within the South African retail banking space. Additionally, the bank can easily customize their omni‑channel offering according to customer needs – not every customer needs every feature. With the microservices architecture, it’s easy to deploy the right features to the right customers.
Better Scalability Through Flexible Deployment
The monolithic architecture made scaling difficult. When the engineers needed more load‑balancing capacity, they had to deploy additional appliances. When they needed more application servers, they physically had to add more hardware.
With the new microservices architecture built on a container‑based framework, scaling in response to changing demand is quick and easy. Because NGINX Plus is deployed within a Docker container, AAfrican Bank developers can spin up new services that are automatically available to requests coming to the NGINX Plus service within the container. This means services can be stateless, ephemeral, and easily scaled in response to user or application demand. In addition, the bank has deployed a flexible NGINX conf templating architecture within this model, which by means of customized scripts can be configured dynamically (via available services gleaned through the Docker API) when the instance is spun up, obviating the need to document and retain specific configuration files. All in all, the NGINX Plus-centric microservices architecture provides a level or reliability the bank didn’t have before.
Enhanced Organizational Agility
The retail bank market is highly competitive in South Africa. African Bank is a smaller entrant in a market dominated by five larger banks. The ability of banks to launch compelling digital features is critical in providing superior service and retaining customers. The previous monolithic architecture made deployment of new features very inefficient: developers often had to traverse significant bureaucratic hurdles or engage with very long testing cycles to launch new services, resulting in time-to-market delays. By moving to a microservices architecture with NGINX Plus at its heart, developers now have much more autonomy in developing and deploying features, resulting in significant efficiency gains and meeting one of AAfrican Bank’s core tenets: “be agile.” Being able to deploy features quicker enables them to deploy more features, helping African Bank stay competitive with their omni‑channel platform.
About African Bank
Founded in 2016, African Bank is a retail bank providing consumer banking services within the South African market.





